A distinctive feature of children is that they perceive any information better in games, since the gaming component increases interest in the process, enhances attention and concentration, and repeated repetitions allow even the most absent-minded kids to absorb knowledge. The competitive moment is very important for born leaders. During the game, a child’s character, peculiarities of imagination and thinking, activity, emotionality, level of social adaptation and a progressive need for contact and communication are revealed.
Didactic games for speech development are a special form of education for preschool children, which allows you to enrich, improve, activate and consolidate vocabulary in the process of play - one of the most important means of harmonious formation and education of a child’s personality.
Depending on the material used, didactic games for speech development are of the following types:
- Games with objects - toys, improvised and natural materials;
- Board games using printed materials;
- Word games.
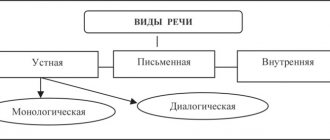
Speech development through didactic games
The development of speech through didactic games occurs by replenishing vocabulary, teaching in a playful way the skills of using words (activating vocabulary), and improving communication skills.
During the period of preschool preparation, the child needs to master a vocabulary that allows him to communicate without problems with peers and adults, successfully acquire school knowledge, and understand the material presented (the content of literary works, the formulation of mathematical problems, etc.). Therefore, the main task of preschool education is the maximum development of speech, which occurs more effectively and efficiently through didactic games.
Didactic games for speech development successfully solve the following problems in preschool education of children:
- Provide quantitative accumulation of vocabulary necessary for full communication;
- Helps in understanding the meanings of words and their correct use with other words;
- Allows you to master the general meanings of words based on identifying common characteristic features of objects, actions or phenomena;
- Improve figurative thinking and its expression by verbal description, thanks to the use of special speech constructions;
- As cognitive abilities develop, didactic games for speech development help expand the objective conceptual content of words;
- Some games with ethical tasks, along with improving vocabulary, teach the inclinations of social ethics and morality;
- Stimulate the imagination, activating and enriching the preschooler’s vocabulary in an entertaining playful way;
- Develop logical and imaginative thinking necessary to solve assigned game problems;
- They not only help expand your vocabulary, but also actively introduce new words into everyday communication.
The vocabulary of a preschooler is significantly inferior in volume to the vocabulary of an adult. The main task of speech development through didactic games is to quantitatively enrich the child’s vocabulary by increasing the volume of accumulated knowledge about the world around him, to activate and teach him to use it competently.
From work experience: The role of didactic games in the development of children’s speech
“The game is a huge bright window,
Through which into the spiritual world of the child
A life-giving stream of ideas pours in,
Concepts about the world around us."
V.A. Sukhomlinsky.
Play occupies a special place in a child’s life. Play is the main activity of children. Through the power of imagination, playful actions, roles, and the ability to transform into an image, children create a game. In games there is no real conditioning by circumstances, space in the decision. Children are the creators of the present and the future. In every era of social development, children live what the people live. But the world around him is perceived differently by a child than by adults: a child is a “newbie”, everything for him is full of novelty and meaning; a child in a game of “discovery” of something that has long been known to an adult. Among the various games I play in kindergarten, didactic games occupy a significant place. A didactic game allows children to be introduced to current life in forms of intellectual and active practical activity, moral and aesthetic experiences that are accessible to them. Didactic games, as a unique learning tool that meets the child’s characteristics, are included in all preschool education systems.
The first didactic games were created by folk pedagogy. Until now, some of the favorite games for children include folk games: “Forfeits”, “Colors”, “What flies?” and others. They contain a lot of funny jokes, humor, and at the same time they require intense mental work, competition in intelligence, and attention from children. The system of didactic games for kindergartens was first created by F. Frebel. he highly appreciated the game and considered it the most important means of raising and teaching a child. The modern system of didactic games was created by U.I. Tekhaeva, has developed a number of games for getting to know the environment and developing speech.
Children can be shy, indecisive, and uncommunicative. To solve this problem, didactic games were used. Through the game, work was aimed at concretizing children’s knowledge, at forming ideas about objects and phenomena of the surrounding reality in speech development classes.
I set a goal : to make the lesson on speech development emotional, effective, allowing the child to gain his own experience with the help of a didactic game.
To solve the problem and achieve the goal, the following tasks :
- Develop the ability to generalize objects, accurately determine the quality of objects.
- To develop voluntary attention in children and focus on the goal.
- Develop fine motor skills of the fingers.
- Teach children to clearly express their thoughts and develop logical thinking.
- Build self-confidence in children.
A thematic plan was also drawn up. When selecting topics, seasonality was taken into account. For example: in the fall I planned games such as “What grew in the garden”, “Which branch did the children come from”; in winter “Who winters how”, “What time of year”; in the spring “Decorate the meadow with flowers”, “Choose the right picture”; in summer “Wonderful bag”; “Find by description.”
Understanding the importance of didactic play in the development of children’s speech and in order to increase interest in the game, I adhere to the following requirements.
- A didactic game should provide exercises useful for mental development.
- The task should be exciting, the solution of which requires mental effort and overcoming difficulties.
- The game should maintain the emotional mood of children and their satisfaction.
Three types of didactic games are used in speech development classes.
- Games with objects (toys, natural materials).
- Desktop-printed.
- Word games.
Games with objects are most accessible to children, since they are based on direct perception and correspond to the child’s desire to act with things and thus get to know them.
The content of board and printed games is varied. They are based on the principle of clarity (image). With the help of paired pictures, children became familiar with individual objects (dishes, furniture, animals, birds, vegetables and fruits, their qualities and properties).
Using “lotto”, the idea of seasonal phenomena was clarified. For example, the lotto “Seasons”, about various professions “Who needs what?”. Word games were widely used in speech development classes. These games are of great importance for the development of the child’s thinking “Finish the sentence”, “Say the word”. Children learned to express independent judgments, draw conclusions, draw conclusions, and notice logical errors. The children really enjoyed making up stories. These games are good because they caused cheerful laughter and developed a sense of humor.
The didactic game helped children learn new material and consolidate what they had learned. The didactic game was organized according to plan during the hours of speech development classes, in addition, during the hours allocated for games. In the morning hours, the game helped create a good, joyful mood in the children for a long time. Also in the morning, didactic games were offered individually to consolidate the sound culture of speech. We learned to correctly identify the sounds of pronouncing pure talk, nursery rhymes, and counting rhymes. To ensure that the mental activity of the players does not decrease and interest in the task at hand does not decrease, the game should last from 10 to 20 minutes.
To relieve visual stress, physical exercises were carried out in a playful way. In order for a child to develop, it is necessary to create conditions for this. The group was equipped with a didactic area where children used a variety of materials with which they played individually and in small groups at will. The selection of games and material was selected taking into account the requirements for clarity. The game should preserve the emotional mood of children, their ease, the experience of joy from the game process and the feeling of satisfaction from solving the problems posed in it. For example: in the game “Shop”, “Who will collect things faster.” The children formed an idea of the subject. In the game “Find a Pair,” children, moving the arrow on the disk, learned to select words that sound similar: bear-bowl, com-catfish, etc.
During the game, a friendly attitude towards each other is cultivated; in no case should violence be allowed against the loser. A losing child is instilled with faith in his own strength and the opportunity to correct his mistake.
In order for the upbringing of children through play to be successful, the necessary conditions are created:
- Sufficient time is allocated for games.
- A calm environment is created.
- appropriate didactic games are selected.
When selecting, first of all, availability, repeatability, gradualness, task completion, and seasonality are taken into account.
In play, the child should be able to act independently, gaining his own, effective and sensory experience.
By observing children's independent games, their knowledge, level of mental development, and behavioral characteristics were revealed. This suggested which games were useful for the child, what the child was strong in, and what he was lagging behind.
I would like to note in my work the close relationship with parents. A correct understanding by parents of the tasks of upbringing and teaching, knowledge of some of the methodological techniques used in the development of children's speech, undoubtedly helped in organizing didactic games at home. Parents received knowledge through conversations, consultations, parent-teacher meetings, and newspapers for parents.
For example: the “Homework” section, where parents are given practical recommendations on developing speech skills.
The “Home Games Library” section was interesting and useful; here parents became acquainted with didactic games to consolidate various speech skills. The material for this section was selected and developed, taking into account the heavy workload of parents with household chores. It is recommended to play with children even in the kitchen.
For example: using game exercises to develop fine motor skills, the didactic game “Helping Mom,” etc.
Since playing with fingers stimulated and accelerated the process of speech and mental development of the child. A game is offered to enrich the vocabulary, for example: “Let’s look for words in the kitchen” or “I’ll treat you.”
Parents were convinced from experience that playing together with their children helped them get to know their children better, understand the characteristics of their character and behavior, and get closer to them. You should always find time for such communication with children.
So, during independent games, a diagnosis was carried out, and I was convinced that through the didactic game I was able to develop organized skills in the children.
The children became attentive and learned to focus on their goals. They began to express their thoughts faster. Through didactic games, children have accumulated positive experience of good feelings and acts of mutual assistance. The children have become more confident.
Thematic plan.
September
- D/i “What grew in the garden?”
- D/i “What time of year.”
- D/i “Wonderful bag”.
- D/i “Find by description.”
October
- Do I need to learn to speak?
D/i "Let's play together."
- Sound culture of speech: the sound “s”.
D/i "Whistle".
- Learning to listen and speak.
D/i "Toy Store".
- Learning to read expressively a poem by M.Yu. Lermontov
“Sleep, my beautiful baby.”
D/i “Put the doll to sleep.”
November
- We learn to reason and talk.
D/i “Guess by the description.”
- Sound culture of speech: the sound “z”.
D/i "Rings - buzzes."
- Literary kaleidoscope.
D/i “Guess by the description.”
- We look at and select souvenirs.
D/i “Make no mistake.”
December
- Travel to Africa.
D/i “Guess by the description.”
- Consideration of the plot painting “This is what Africa is like.”
- D/i “Which one, which one, which one?”
- Sound culture of speech: the sound “ts”.
Learning the folk song “Zarya – Zaryanitsa”.
January
- Journey to a fairy forest.
D/i “I am an old man, a forest worker.”
- Examination of the plot picture “The Forest and Its Inhabitants.”
- Sound culture of speech: the sound “sh”.
- Dialogue with the brownie “New riddle.”
- Memorizing the poem by A. Barto “I know what I need to come up with.”
D/i “Say a word.”
February
- Journey to the meadow kingdom - the state.
Repetition of L. Modzalevsky's poem "The Moth".
D/i “Complete the sentence.”
- Sound culture of speech: the sound “zh”.
D/i “Render a guess, we will guess.”
- Memorizing the poem by Yu. Kushak “Little Deer”.
D/i “Be careful.”
March
- Travel to the Far North.
The game is dramatization.
- Looking at the plot picture.
North and tundra".
D/i “Find what I’ll describe.”
- Learning the Russian folk song “Grandfather wanted to cook fish soup.”
D/i "Guess what's in the bag."
- Literary kaleidoscope.
D/i “Come up with another word”, “Riddle game”.
April
- Sound culture of speech: the sound “sch”.
D/i “What is planted in the garden.”
- Journey to the underwater kingdom - the state.
D/i “Guess it.”
- Sound culture of speech: the sound “l” (l).
D/i “When it happens.”
- Literary kaleidoscope.
D/i “Tree, shrub, flower.”
May
- Sound culture of speech: the sound “r”.
Memorizing G. Kruzhkov’s poem “Rrrs”.
- D/i "third wheel".
- Literary kaleidoscope.
D/i “Travel”, “Kind Word”.
- Memorizing the poem "Dandelion".
D/i “Do you remember these poems?”
D/i “Give me a word.”
Didactic games for the development of speech for children from two to three years old
At the age of 2-3 years, the child must master the names of items of clothing, dishes, furniture, toys that surround him in everyday life and arouse his interest. During this period, the names of the actions performed with these objects are also mastered.
The task of educators during this period, with the help of didactic games, is to teach children to name and distinguish:
- Parts of objects, parts of the body of animals and humans;
- Different sizes;
- Primary colors;
- Main taste qualities;
- Some physical qualities and properties.
It is necessary to develop the ability of children to denote in one word a group of similar objects united by a common feature and to distinguish between similar groups of objects.
It’s good at this age to start teaching your child to talk on the phone with an invisible interlocutor. This is a kind of didactic game that develops not only vocabulary, but also abstract thinking, the ability to express one’s thoughts without the help of gestures. You should structure such a conversation correctly, asking simple questions that do not require complex answers; you can make a telephone conversation, for example with your grandmother, a daily ritual.
Didactic games for speech development are also recommended, the essence of which is clear from the name - “Name it correctly...”, “What has changed...”, “What does it consist of...”, etc.
The main goal of such games at this age, while improving vocabulary, is to instill in the child an interest in vocabulary activities.
Speech development through didactic games at four years old
At four years of age, the child’s vocabulary is further expanded, with a more detailed delving into the details and characteristics of the world around him. This is necessary to enhance differentiated perception and deepen knowledge about the characteristics of objects, their purpose, structure and expand the understanding of qualities and properties. At this age, the baby must learn the basic techniques of orientation in space and time, master the corresponding words (morning, evening, forward, backward, first, then). Didactic games for speech development, recommended for 4-year-old children, should begin with the phrases “What first, what then...”, “When it happens...”, “What has changed...”, “What will happen if...”, “What can be done with... ", "What can you do with...", "More than...Less than...", "One...many..." and the like.
It’s good if the child talks every evening about how he spent the day, what he played and with whom, what he saw and did. By answering parents' leading questions during role-playing games using their favorite toys, the baby will develop faster, expanding his vocabulary and improving his ability to use it.
Speech development through didactic games at 5-6 years old
Senior preschool age is a period when children, with the help of didactic games, actively acquire spoken language, mastering vocabulary, phonetics, and grammar. The vocabulary expands, based on in-depth knowledge of the surrounding world. The main task of didactic games for the development of speech at this age, along with further replenishment of the vocabulary, is to teach the child dialogic and monologue speech.
In a playful way, special communicative situations should be created in which the child must maintain a conversation, starting and conducting a dialogue. There are game moments in which the adult and the child change places and the child asks questions.
During the period of preschool preparation, it is important to teach the child narrative speech, the ability to compose and pronounce monologues - for this, in the form of a game, you can offer to describe specific situations, such as a long journey, a visit to the zoo, a fairytale journey, with a detailed description of the details (objects, properties, qualities, actions and etc.).
Didactic games for speech development contribute to the realization of the characteristic age-related opportunities for the harmonious mental development of preschoolers, preparing them step by step for school life.
Speech development in preschoolers through play
Development of speech skills in preschool educational institutions through play
Preschool age, as is known, is a period of intensive development of the child, and timely acquisition of correct speech, including its active use, is one of the main conditions for the normal psychophysical development of the child, the formation of a full-fledged personality, and preparation for school. Currently, the number of preschool children who experience difficulties interacting with peers has increased. L.S. Vygotsky believed that “with the help of speech, a child for the first time becomes capable of mastering his own behavior, treating himself as if from the outside, considering himself as a certain object. Speech helps him master this object.” In preschool age, play is the leading activity of the child, an effective method and one of the forms of teaching and upbringing that stimulates the speech activity of children. Games with words and sounds for children are not only attractive, but also useful. Speech games are aimed at developing speech in children, clarifying and consolidating vocabulary, and developing correct sound pronunciation. At the same time, they are the basis for enhancing cognitive activity and developing mental abilities. Preschoolers develop the ability to express their opinions, draw conclusions, and apply new knowledge in various life situations. Speech games are of great importance for the development of children's speech and thinking; they activate, enrich their vocabulary, improve phonemic hearing in children, and instill interest and love for language.
Games for the development and enrichment of an active speech vocabulary
A) Complete the sentences - In the summer, the leaves on the trees are green, and in the fall.. - A bunny in the summer ...., and in the winter ... - Mushrooms grow ..., and cucumbers - on ... - The fish lives in ..., and the bear - in... - Sugar is sweet, and lemon... - It’s light during the day, and at night... B) Finish the sentence Children take turns finishing each of the sentences: I want... I can... I will help... I will bring... I will sing... C) Tell me which one - Pencil - new, big, beautiful, ribbed, colorful, thin, durable... - Autumn leaf, yellow, large, small, fallen... - Flower - fragrant, spring, forest, bright, small... - River - fast, transparent, deep, clean , wide... - Mom is kind, gentle, sweet, affectionate, hardworking...
Games for recognizing parts of speech, finding out the relationship between them
A) Cheerful family Name the animals and their babies correctly. - Mom is a fox, dad is a fox, the kids are foxes. - Rooster, hen, chickens. - Cat, cat, kittens. - Goose, goose, goslings. - Bear, mother bear, cubs. B) Big - small Choose an affectionate word. - Mom - mommy, - vase - vase, - cat - cat, - sun - sun, - river - rivulet, - birch - birch, - leaf - leaf. C) Catch the ball The teacher names a noun and throws the ball to the child.
The child forms an adjective from the proposed word and returns the ball to the teacher. - spring - spring, - sun - sunny, - birch - birch, - linden - linden, - rain - rainy. Speech games for developing the ability to express one’s own opinion A) Agreement - disagreement The task of the teacher is to develop in children the ability to affirm or dispute a thesis, to justify their opinion. Educator. It will be rain today. Children. No, it won’t, because the sky is clear. Educator. All the birds fly away to warmer climes. Children. No, some remain for the winter (sparrow, crow, jackdaw). Educator. This is a fish. Children. No, it's not a fish. This is a mouse. A fish can't run, but a mouse can. The mouse has ears. but the fish do not. B) Fable story The task of the teacher is to teach how to determine the topic of reflection using inserted constructions “I think”, “I know”, “it seems to me”, “in my opinion”; deny inappropriate phenomena using subordinating conjunctions “because.” After listening to the tall tales, children identify the inconsistencies they noticed. In summer the sun shines brightly, so the children went for a walk. They made a slide out of snow and started sledding. Then they made a snow woman out of sand. That's how much fun the kids had! Autumn has come because the green leaves have begun to fall. The children went on an excursion to the lake. There they saw a lot of interesting things. There were two perches and a crayfish sitting on the shore of the lake. When the children came closer, the crayfish and perches fell straight into the water. Near the lake there were many birch trees, and on their branches there were mushrooms hidden among the green leaves. The children jumped up and picked a few mushrooms. That's how many interesting things they saw on the excursion! Games for improving correct sound pronunciation, developing phonemic hearing A) New word formation In a word, replace the vowel sound [y]: squirrel - bun, river - hand, give - blow. Replace the vowel sound [o]: sam - catfish, frame - Roma, cash - scythe, race - dew. BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. “Education of sound culture of speech in children in preschool educational institutions” Author: L.R. Bolotina, N.V. Miklyaeva, Yu.N. Rodionova. 2. Speech therapy E.N. Krause 2002 3. A.I. Maksakov, G.A. Tumakova “Teach by playing” 2005.
We recommend watching:
Speech games for the development of coherent oral speech for younger schoolchildren Summary of a lesson on speech development for the older group Speech games for children 5 - 9 years old Consultations for preschool teachers. Using oral folk art for speech development
Similar articles:
Games for the development of speech breathing in the middle and senior groups
Speech development in children 3-4 years old with developmental disabilities based on Suteev’s fairy tales
Stages of speech development in a child
Tasks in pictures for speech development for children 3-5 years old
Exercises for speech development in children 4-5 years old