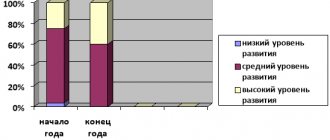
Innovations in a modern preschool educational institution
Management structure: development program.
Organizational structure: diagnostics – forecasting – organization – practice – generalization – implementation.
Life cycle of innovations.
1. Discovery stage: inception, emergence of the concept of innovation.
2. Development: invention, creation of an innovation embodied in an object (material or spiritual).
3. Implementation of innovation: practical application, refinement, lasting result, independent existence of innovation subject to receptivity.
4. Dissemination, replication: widespread introduction, diffusion or dominance of an innovation in a specific area, the innovation ceases to be such, loses its novelty.
5. An effective alternative, or its replacement, or a reduction in the scope of application of the innovation.
The linearity of the stages may be violated: within one stage others are permissible, breaks, phase loss, etc. are possible. From the fourth stage there is continuous improvement.
From the point of view of interaction with the environment, the life cycle includes:
· start;
· fast growth;
· maturity;
· saturation;
· a crisis.
Stages of perception of innovation according to Eric Rogers.
1. Familiarization: a person hears about an innovation for the first time and is not yet ready to receive additional information.
2. Appearance of interest: interest + search for additional information. While the internal need to accept innovation is impossible (the subject does not try it on himself).
3. Evaluation: the subject tries on the innovation and decides whether to use it, looks for clarifying information, and critically evaluates it.
4. Approbation: portioned application in practice, depending on the result - acceptance or refusal.
5. Final perception: the decision follows to adopt the innovation and widely use it in practice (through evaluation of the results of the fourth stage).
The presented parameters of the innovation process need to be adapted to the preschool education, which is currently characterized by the dynamics of individual areas and processes. It is innovations that are designed to synchronize and integrate the main aspects of the functioning and development of preschool educational institutions in order to ensure the quality of preschool education.
Conclusion
The ongoing changes in the preschool education system are due to the objective need for changes that are adequate to the social development and evolution of the educational system, which is reflected in the awareness of the pedagogical community of the need for serious changes in the functioning of the institution.
The search and development of innovations that contribute to qualitative changes in the activities of preschool educational institutions is the main mechanism for optimizing the development of the preschool education system. Many researchers associate the development of preschool educational institutions with the processes of targeted development and creation, implementation and mastery, dissemination and stabilization of innovations, which determine its qualitatively new state. It should be noted that the degree of innovativeness of education is determined by the level of development of society and dictated by the level of “underdevelopment” of education. In other words, innovation occurs where and when there is a need for change and the ability to implement it.
Main directions of innovative development of preschool educational institutions
The article presents an analysis of the main directions of innovative development of preschool educational institutions, defines the tasks of pedagogical activity in an innovative mode, examines the content, methods and forms of implementation of innovative projects and programs in the activities of the teaching staff.
Key words: innovation, innovative development, preschool educational institution, teaching staff.
The article presents an analysis of the main areas of innovative development of pre-school educational institutions, identifies the tasks of pedagogical activity in an innovative mode, examines the content, methods and forms of implementing innovative projects and programs in the activity of the pedagogical collective .
Key words: innovations, innovative development, kindergarten, teaching staff, educational services.
Federal State Educational Standards (FSES) for preschool education guide teachers to search for favorable conditions for the development of children; choosing effective methods and means of training and education. The content of preschool education is enriched with new procedural skills, the development of abilities to handle information, creative solutions to problems of science and social practice, the individualization of educational programs that encourage teachers to innovative activities, creative search, professional self-realization in research work.
Research by scientists (I. A. Kopylova, V. S. Lazareva, V. Ya. Laudis, V. P. Panasyuk, Yu. V. Smirnova, E. N. Stepanova, G. V. Yakovleva, etc.) shows that the modern educational process in kindergarten requires a transition to innovative models of educational activities. This means that many agreed and coordinated innovations must be introduced into the pedagogical systems of preschool educational institutions, thanks to which educational institutions for preschool children will be able to achieve higher results than before in the upbringing and development of children (V.V. Kozlov, N V. Kuzmina, A. K. Markova, etc.).
From the point of view of N.V. Miklyaeva, the following can be identified as promising areas for innovative development of a preschool educational institution:
‒ active construction of a developing subject-spatial environment that contributes to improving the quality of education in a preschool educational institution;
‒ studying pupils throughout the entire period of children’s stay in kindergarten in order to ensure a person-oriented approach;
‒ expanding cooperation between preschool educational institutions and other social institutions;
‒ strengthening interaction with parents;
‒ improving the material and technical base of a preschool educational institution [2, p. 21].
One of the areas of innovative development of a preschool educational institution is to increase the professional competence of teachers and provide them with timely methodological assistance [1, p. 32]. In this case, the tasks of innovative activity of a preschool educational institution are aimed at:
‒ increasing the professional readiness of teaching staff to implement innovative projects through the creation of a system of continuous professional development;
‒ creating conditions for expanding teaching activities and additional educational services;
‒ organizing the work of the teaching staff in development mode;
‒ increasing pedagogical competence, unlocking the creative potential of teaching staff and other specialists of a preschool educational institution.
The tasks of organizing innovative activities in preschool educational institutions are implemented in the following areas.
The first direction: analytical, diagnostic.
Purpose, content: identifying professional problems in the activities of teachers.
Second direction: design.
Purpose, content: development of projects for innovative activities in a preschool educational institution.
Third direction: psychological and pedagogical.
Goal, content: improving the psychological and pedagogical culture of teachers in the process of implementing innovative activities, familiarization with advanced pedagogical technologies, discussion and implementation of innovative projects.
Fourth direction: controlling.
Purpose, content: monitoring and assessing the effectiveness of the implementation of innovative projects in a preschool educational institution [4, p. 73].
To carry out innovative activities in a preschool educational institution, the following conditions are implemented:
‒ motivating teachers to participate in the development of projects for innovative activities of a preschool educational institution;
‒ conducting courses and methodological associations on the problems of developing innovative projects in a preschool educational institution;
‒ organization and participation in competitions, shows, exchange of experience among teaching staff, both in preschool educational institutions and in other preschool educational institutions of the city and region.
Literature:
- Lazarev V.S. Pedagogical innovation: object, subject and basic concepts / V.S. Lazarev, M.S. Tarantseva, O.G. Chuiganova // School Director. — 2014. — No. 4. — pp. 12–15.
- Miklyaeva N.V. Innovations in kindergarten / N.V. Miklyaeva. - M.: "Iris Press", 2012. - 186 p.
- Mukhamadeeva V. S. Assessing the readiness of teachers to implement the professional standard / V. S. Mukhamadeeva // Perspectives of Science - 2016. - No. 7. - P. 26–32.
- Fundamentals of innovative design: textbook / edited by V. A. Sergeev. - Ulyanovsk: UlSTU, 2015. - 246 p.
- Piskareva I. E. Methods for diagnosing teacher readiness for innovative activities / I. E. Piskareva. - M.: MGKU, 2012. - 60 p.
- Yakovleva G.V. Pedagogical conditions for increasing the effectiveness of methodological work in an innovative preschool educational institution: Dis. Ph.D. ped. Sciences / G. V. Yakovleva. - Chelyabinsk, 2009. - 248 p.
Article from work experience “The project method is an innovative form of activity in preschool educational institutions”
UDC 373.24
Shiryaeva Nadezhda Vasilievna
Municipal preschool educational institution "Kindergarten No. 1 "Fairy Tale",
Sovetsky Republic of Mari El
Project method –
innovative form of activity in preschool educational institutions
In this article, the project method is interpreted as a unique means of ensuring cooperation and co-creation between children and adults. Experience in introducing project activities into the child upbringing and education program is presented.
Key words:
a set of interrelated activities, interaction with parents, support for children’s initiatives, methodological activity of the teacher.
Major changes have occurred in the preschool education system.
Firstly, a new “Law on Education in the Russian Federation” has been adopted.
Secondly, the federal state educational standard for preschool education came into force. Preschool childhood becomes the main and most important stage, when the foundations of personal development are laid: physical, intellectual, emotional, communicative. This is the period when a child begins to realize himself and his place in this world, when he learns to communicate, interact with other children and with adults.
Thus, reforming preschool education requires the introduction of innovative technologies into the educational system of preschool institutions. All this requires teachers to have a new set of skills - to design the development of their own educational activities.
Therefore, a unique means of ensuring cooperation and co-creativity between children and adults is design technology and the use of the project method in preschool educational institutions with integration in various educational fields. The origin of this method occurred in the second half of the 19th century. This new didactic method was developed by the American educator John Dewey. According to the American teacher, this method not only prepares the child for life in the future, but also helps organize it in the present.
The project method was also reflected in the ideas of domestic scientists (N.K. Krupskaya, S.T. Shatsky, M.V. Krupenina, etc.), who believed that it could ensure the development of creative initiative and independence in learning, the connection of theory with practice. Subsequently, projects widely became part of pedagogical practice; they often completely replaced the curriculum, so in the 30s. this method was banned in Russia.
Currently, the project method is considered by science as a cycle of innovative activity and is one of the promising pedagogical technologies that have the appropriate characteristics, functions and structure. In the modern understanding, the project method in no way replaces the existing education and training program, but only complements it.
Pedagogical design is a way of organizing the pedagogical process, based on the interaction between teacher and student, as a way of interaction with the environment, a set of interrelated activities for purposeful changes in the pedagogical system over a given period of time.
The main function of design is to develop a plan and select means for further targeted actions.
Here are some points of the Federal State Educational Standard that can be implemented through project activities:
— assistance and cooperation of children and adults, recognition of the child as a full participant (subject) of educational relations;
— supporting children’s initiative in various activities;
- formation of cognitive interests and cognitive actions of the child in various types of activities;
— professional development of teaching staff;
— interaction with parents on issues of the child’s education, their direct involvement in educational activities, including through the creation of educational projects together with the family based on identifying needs and supporting the family’s educational initiatives.
Thanks to the project method, the educational process is holistic and not broken into parts. This allows the child to “live” the topic in different types of activities, without experiencing the difficulty of moving from subject to subject, to assimilate a larger amount of information, and to comprehend the connections between objects and phenomena.
In my professional activities, I also use the project method. At this point in time, I have implemented 3 projects with my students: “Wonderful Bag”, “Magic Button”, “Give Kindness”. The last project I implemented was the educational and creative project “Give Kindness.” The project is group, long-term.
The goal of the project is to create a system of work to instill positive character traits in children and motivate them to do good deeds.
The novelty of the project is to increase children’s motivation to do good deeds through cooperation with the volunteer union. In the process of implementing the project, we collaborated with the volunteer union of Secondary School No. 3 in Sovetsky.
To achieve the goal, various forms of work were carried out with children: conversations, games, reading fiction, watching cartoons, educational activities, entertainment, etc.
International Volunteer Day is celebrated annually on December 5th. Therefore, it was on this day that the guys from our group and I solemnly joined the ranks of volunteers.
As part of the project, at the final stage, several events were held: “Let's cure books”, “Take the kids for a ride - give them joy”, “Bird feeders”, “Hand in waste paper - save a tree!”, Drawing competition “I See the World with Kind Eyes”.
This project expanded preschoolers’ ideas about kindness, its role in the life of every person, fostered humane feelings, a friendly attitude towards the world around them, and developed the ability to help and sympathize with their immediate environment. The children actively participated in all stages of the project and rejoiced at the good deeds they performed.
In the future, we will implement a child-parent project, where the child, together with his parents, will find and use the necessary information for his own purposes.
Thus, project activity as one of the forms of improving the skills of teachers is quite effective and innovative. The methodological activity of teachers has increased significantly. As practice has shown, the introduction and implementation of the project method expands the educational space, gives it new forms, makes it possible to develop the child’s creative, cognitive thinking, lays down the positions of independence, activity, initiative in finding answers to questions, systematizes information, and allows the use of acquired knowledge and skills and skills in games and practical activities, which contributes to the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard for Education.
Bibliography.
1. Kiseleva, L.S. Project method in the activities of a preschool institution [Text]/L.S. Kiseleva, T.A. Danilina, T.S. Lagoda, M.B. Zuykova // Manual for managers and practical workers of preschool educational institutions. – M.: Arkti, 2005. – 96 p.
2. Mikhailova, I.V., Kalikova, E.A., Kolodyazhnaya, M.A. Project method in preschool educational institutions, as an innovative pedagogical technology // Young scientist. - 2016. - No. 23.2. — P. 74-76. — Access mode: https://moluch.ru/archive/127/35349/
3. Petrova, V.I., Stulnik, T.D. Moral education in kindergarten. M.: Mosaic-synthesis, 2008.- 80 p.
4. Urmina, I.A. Innovative activities in preschool educational institutions: program. - method. provision: hand aid. and adm. workers - M.: Linka-press, 2009. - 90 p.
Model of an innovative kindergarten
Innovative activity changes the traditional management pyramid and puts the teacher and students, heads of educational institutions, senior educators, scientific and methodological assistants, and their professional demands and needs at the forefront. It is not administrative will and pressure that become the driving force for the development of an educational institution, but the real creative potential of teachers: their professional growth, attitude to work, and ability to reveal the potential of their students.
However, pedagogical practice indicates that preschool educational institutions are not sufficiently prepared for the selection and evaluation of positive innovations in preschool education, for the development and implementation of innovative programs and technologies, for their high-quality implementation in working with children. This circumstance quite convincingly indicates that there is a contradiction between the socially determined need to improve the professional competence of teachers of innovative preschool educational institutions and the real state of innovation activities designed to ensure the readiness of teachers to innovate.
Despite the fact that the problems of innovative pedagogical activity have widely and firmly entered into the life of preschool educational institutions, regulatory and instructive-managerial support for the processes of updating management activities and methodological work in preschool educational institutions, increasing their effectiveness in the context of the implementation of innovations is clearly not enough. Existing approaches to organizing methodological work are not focused on the process of updating preschool education. That is, the system of methodological work today is inadequate to the innovative processes in which preschool educational institutions teachers are involved. The practice of innovation requires the transfer of management activities and methodological work of the preschool educational institution to its new state - the innovative space of the preschool educational institution.
In this regard, the need arose to develop a program.
Innovation program at preschool educational institutions
The program is based on concepts such as:
Innovative management activities,
according to Davytkina E.V., this is the activity of the head of a preschool educational institution to create, develop, master innovations in the content of management functions, methods used, organizational structure, introducing innovations into practice in order to increase the efficiency of management and development of a preschool educational institution.
This leads to the definition of management innovations
as targeted changes associated with the introduction of new elements into the management cycle, organizational structure and management methods of the head of a preschool educational institution, which leads to the development of a management system for a preschool educational institution. The introduction of management innovations leads to the renewal of the management activities of the head of a preschool educational institution, which acquires an innovative character.
Stages of implementation of an innovative project
Completed:
Ardyntsov A.A., Deputy Director for Education and Resource Management, Municipal Budgetary Institution of the Children's and Youth Sports School of the village. Svetly, Svetlinsky district, Orenburg region
Project No. 3. Stages of implementation of an innovative project
Present the stages of project implementation, results for each stage, indicators.
Information and communication technologies (ICT) are increasingly penetrating various areas of educational activity every day. This is facilitated by both external factors associated with the widespread informatization of society and the need for appropriate training of specialists, and internal factors associated with the dissemination of modern computer hardware and software in educational institutions, the development and adoption of state and interstate programs for informatization of education, and the emergence of the necessary experience in informatization among more and more teachers.
In most cases, the use of information technology has a real positive impact on the intensification of the work of school teachers, as well as on the effectiveness of schoolchildren’s education.
The innovative potential of the project lies in its implementation, the ability to directly influence the organization and provision of the educational process, the optimization of educational technologies, close communication with the parent community, the ability to quickly adjust the educational process, and individualize its forms.
One of the most important tasks in the development of the education system in the Orenburg region is to ensure accessibility and transparency of school activities.
Open educational environment policy:
- makes it possible to coordinate the requirements and requests of participants in the educational process;
- allows for the formation and development of a system of social partnership, ensures public involvement in school activities
- allows you to create a positive image of the school, ensures the attraction of new qualified teaching staff;
- ensures the positioning of the school in the market of educational services, informing about activities, creating a strong positive reputation - a guarantee of the successful development of the school.
Thus, this innovative project is the construction of a new educational environment with high intensity of various forms of social and educational partnership of teachers, parents and children using the potential of modern media and communication, including maximum information technology resources.
Objective
of the project:
- Using the policy of an accessible and open educational environment as a resource for the development of an educational organization in order to increase the efficiency of the educational process.
Project objectives:
- Formation of information competence of participants in the educational process (training of teaching staff with new tools and resources of information and communication technologies);
- Increasing the participation of the parent community in the system of state and public management of the educational process;
- Establishing partnerships with educational institutions and other organizations;
- Transition to an electronic form of maintaining school records;
- Creating a sustainable positive image of the school among residents of Olenegorsk and its subordinate territory.
Necessary resources for project implementation
- Scientific and pedagogical
- The methodology of the innovation project consists of systemic, activity and information approaches.
The main purpose of the systems approach is a holistic vision of the object.
Activity approach
provides the construction of methodological foundations associated with the unity of the objective and subjective in the types of activities and interactions “teacher - information means - parent - student”.
Information approach
allows us to determine the information environment, information support for dialogue, and carry out a critical analysis of existing information technologies used to ensure transparency of school activities for society.
- Methodology for socio-pedagogical design and “growing” of new knowledge directly in the process of project implementation, defining the basis for constructing the logic of research and justifying the stages of the project;
- A quality assessment methodology that allows designing changes to the system for assessing educational results and achievements.
- Educational and methodological
To implement the results of the innovative project in other educational institutions, the following educational and methodological “products” will be developed, tested and presented in printed or electronic form:
1) a package of methodological materials for organizing webinars;
2) a model of an information card for the deputy director for educational work to coordinate the actions of all participants in the educational process in the information field of the educational institution;
3) methodological recommendations for interaction in the form of virtual dialogue with parents;
4) materials for diagnosing an innovative project (questionnaires, surveys, individual conversations, ratings, etc.);
5) generalizing the experience of implementing the project as a whole and developing recommendations for educational institutions on the introduction of such innovations into the educational process.
- Organizational
Compliance of teaching staff with the requirements of professional standards (all teachers have completed advanced training courses in information and communication technologies literacy).
Availability of job descriptions for employees, regulations on the procedure for teaching staff to access IT networks and databases, reminders of children’s safe behavior on the Internet, regulations on assessing the effectiveness of teachers’ innovative activities.
Legal
- The concept of introducing modern information technologies
- Order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 25, 2014 No. 2125-r “On approval of the Concept of creating a unified federal interdepartmental system for recording the student population in basic educational programs and additional general education programs”
- The concept of development of a unified information educational environment in the Russian Federation and others.
About the websites of educational organizations
- Order of the Federal Service for Supervision in Education and Science dated May 29, 2014 No. 785 “On approval of the requirements for the structure of the official website of an educational organization on the Internet and the format for presenting information on it”
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 10, 2013 No. 582 “On approval of the rules for posting on the official website of an educational organization on the Internet information and telecommunications network and updating information about an educational organization”
- Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated June 14, 2013 No. 462 “On approval of the procedure for conducting self-examination by an educational organization”
- Federal Law of December 29, 2012 No. 273-FZ “On Education in the Russian Federation”
3. Financial and economic
— attraction of sponsorship funds, voluntary donations;
— participation in open grant competitions.
- Personnel
Creating a team of like-minded people capable of solving assigned tasks and working for results, consisting of:
— school teachers who have experience working as leaders of educational organizations, problem-solving groups, and leaders of project teams involved in innovative activities;
— parents (legal representatives);
— representatives of social institutions, partners, sponsors.
- Logistics
Strengthening and development of the material and technical base of the project through:
— improvement of the existing infrastructure, allowing to increase the efficiency of educational and management activities;
— installation of high-speed Internet (already installed);
Actions taking into account risks and resources
The project is limited in time, resources, territory, target group. Therefore, inevitably something remains outside the scope of vision and influence in the project, both points of growth and problem points.
The following methods were used to identify risks and limitations: brainstorming; discussions; analysis of assumptions. To manage project risks, impacts to reduce each risk were identified and presented in the table.
Project implementation risks
| Risks | Minimizing risks |
| Insufficient development of the environment (lack of elements of information infrastructure to support the project, failures in network communication). Aging of the material base and software of the OS | Equipment of the op-amp, use of freely distributed software |
| Insufficient experience of teachers using computer technologies | Development of a school program for improving ICT competence of teachers |
| The focus of some teachers on traditional forms of organizing activities. Problems of a psychological nature: rejection of the idea of innovation by individual subjects | Promotion of innovative developments, methodological seminars, encouragement of those teachers who introduce innovations. |
| Unpreparedness of the parent community to accept objective results of assessing the quality of education of their children. | Creation of mechanisms for conveying information to the consumer of educational services. |
| The risk of an inadequate reaction to information in a virtual environment, the risk that (by mistake) information will be published that is not intended for public access. | Conducting a dialogue not on publicly available resources, but on specialized ones such as “Network City. Education" on the terms of personalized access. |
| Not all parents have a personal computer or the Internet at home. | Using a paper version of the diary to communicate with parents, printing pages of an electronic diary for parents. |
Expected results of the implementation of the innovation project
For students:
— students’ awareness of the possibilities of virtual communication as an important tool in learning;
— increasing motivation for learning and training;
— the ability to electronically accumulate independently completed work in an electronic portfolio;
— the possibility of expanding the field of interaction with teachers through the use of a virtual component.
For the teacher:
— general growth of information technology competence;
— readiness for new forms of dialogue interaction with participants in the educational process;
— improving the student assessment system;
— increasing opportunities for self-realization in the course of innovation activities.
For parents:
— prompt receipt of pedagogical consultation from the teacher;
- participation in discussing the problems of the educational institution with other parents in the forum and active influence on the course of educational and educational processes in the educational institution.
For school:
— improvement of the educational program;
— openness of performance results;
— strengthening connections between all participants in the educational process through the use of ICT tools;
— increasing competitiveness.
For society:
— demonstration of the exceptional importance of the family for solving the problems of education and socialization of the younger generation in the information society by involving specialists from the parent community in the implementation of the project;
— availability of methodological recommendations for transferring experience to other educational institutions.
Criteria for the effectiveness of project implementation:
• Positive internal and external examination of the program and its testing.
• The number of educational institutions in which this program will be in demand.
• General growth of information and technological competence of participants in the educational process.
• Parents' demand for the proposed forms of virtual dialogue.
• Updating and updating the website of the educational institution.
• Maintaining personal electronic portfolios for students and most teachers.
• Availability of a database of electronic documents.
• Regular (at least once a month) updating of sections of methodological associations of teachers.
• Implementation of telecommunications projects using a “project portfolio”.
• Increased satisfaction with the quality of the educational process among students and parents.
• Parents' satisfaction with the opportunities to receive prompt and high-quality information about school affairs and problems.
• Increasing various forms of involving parents to solve school problems.
• Consistently high status of the educational institution in the area.
Main consumers of the project results
Educational organizations of the Orenburg region.
Project implementation plan by stages
| Stage name | Main events | Predicted result |
| First stage: preparatory | Justification of the relevance of the Project. Creation of working groups in the main areas of work, development of a mechanism for the implementation of the Project, a system for monitoring the progress and results of the Project implementation. Methodological support for the project, development of the regulatory framework. Open discussion of the Project by participants in the educational process. Testing of Project implementation mechanisms and control forms. | Growth of information and technological competence of participants in the educational process. |
| Second stage: practical | Implementation of the main directions of the Project. Identify problems and make adjustments. Summing up the interim results of the Project implementation. Preliminary assessment of the effectiveness of the Project. | Working with interactive formats (survey, forum, guest book). Positive internal and external examination of the project at the school. |
| Third stage: final | Analysis, synthesis and dissemination of results obtained during the Project implementation. Assessment of Project effectiveness. Presentation of the Project in the teaching community | Increasing the information openness of educational institutions. Replication of positive experience of project implementation in the educational institution — teachers use and create distance learning courses and tests - the Internet portal of the educational institution is being updated and expanded - many teachers and students maintain personal portfolios, there is a database of electronic documents, sections of methodological associations of teachers — telecommunications projects are implemented using the “Project Portfolio”. |
Project implementation algorithm
- Creation of working groups on main areas of work
- Creation of the project's regulatory framework
- Open discussion of the Project by participants in the educational process.
- Development of a monitoring system for the progress and results of the Project implementation.
- Development and testing of forms of control over Project implementation.
- Interim analysis of the preparatory stage of the Project implementation
- Publication of Project implementation materials on the school’s official website
- Working with interactive formats (survey, forum, guest book, etc.).
- Internal and external examination of the Project.
- Presentation of positive experience in implementing the project at the educational institution:
— webinar for city schools
— online conference for regional school administrations
— master class for city teachers
- Implementation of AIS “Electronic School”
- Drawing up an analytical report on the implementation of an innovative project
- Public presentation of the Parent Community Project
- Presentation of the Project in the teaching community.
Main planned results of the implementation of the innovation project
| № | Events | Expected Result |
| 1 | Information support of the project | Posting information on the MA website in the form of reports and orders Posting a description of the experience on the Internet on the website of the Education Committee |
| 2 | Participation (representation of experience) in events aimed at ensuring the quality and effectiveness of disseminating best practices for implementing innovative projects | — Speech at the conference “Introduction of the Federal State Educational Standard for basic general education in schools in the Murmansk region: experience, problems, solutions” — Training seminar for school teachers “Possibilities of the AIS “Electronic School” resource” — Master class for school teachers on working with a personal portfolio in the AIS “Electronic School” -Presentation of experience at the August pedagogical conference — Open day for municipal schools |
| 3 | Share of teaching staff participating in the project implementation | 100 % |
| 4 | Development of an internship program | Approval of the developed internship program |
| 5 | Organization of monitoring the demand for materials of innovative activity | Creating a feedback system: — Creation of a forum on the school website to ensure monitoring of the demand for materials; — Creation of a feedback page on the school website in the innovative project implementation section |
| 6 | Conducting consultations for educational organizations and their employees on the project topic | — Network consultation “Maintaining a personal portfolio” in the AIS “Electronic school” |
| 7 | Development of materials (products) necessary for the implementation of the project | Questionnaire for parents to check their understanding of the main points of the innovative project. Internship program |
| 8 | Indicators indicating the effectiveness of innovation activities in an organization | Positive internal and external examination of the program in the first phase of the project. General growth of information and technological competence of participants in the educational process. Updating and replenishment of the OU Internet portal. Maintaining personal electronic portfolios for students and teachers. Updating sections of methodological associations of teachers. Increasing various forms of parent involvement to solve school problems. |